Back
Back
Hydrogen energy is a kind of secondary energy that gradually become one of the important energy carriers for global energy industry.
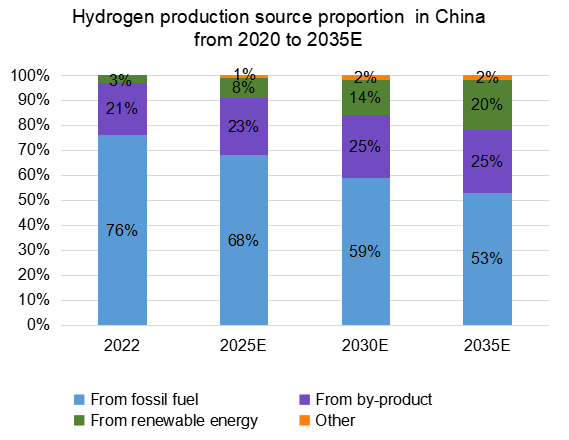
Currently, most hydrogen in China is "gray hydrogen" produced by fossil fuels and industry by-products, of which only a small part can be converted into "blue hydrogen" by combining CCUS technology. Due to the high cost, CCUS technology is not mature, except for some demonstration projects, has not been widely promoted in China. In addition, green hydrogen, water electrolysis technology has not been widely because of its high cost. However, CCUS technology is more likely to achieve continuous cost reduction.TD considers that China’s hydrogen source would gradually transform from gray hydrogen to blue hydrogen in the medium term, while the proportion of green hydrogen would gradually increase in the future.
Hydrogen production cost comparison | ||
Type | Cost | |
From coal | Without CCUS | 1.04-2.15 $/kg |
With CCUS | 1.56-2.80 $/kg | |
From Natural gas | Without CCUS | 1.15-3.73 $/kg |
With CCUS | 1.54-4.97 $/kg | |
From by-product | Coke-oven gas | 1.43-2.29 $/kg |
2.02-3.10 $/kg | ||
Chlor-alkali | ||
From Electrolysis of water | AWE | 1.42-6.15 $/kg |
PEM | 3.15-7.46 $/kg | |
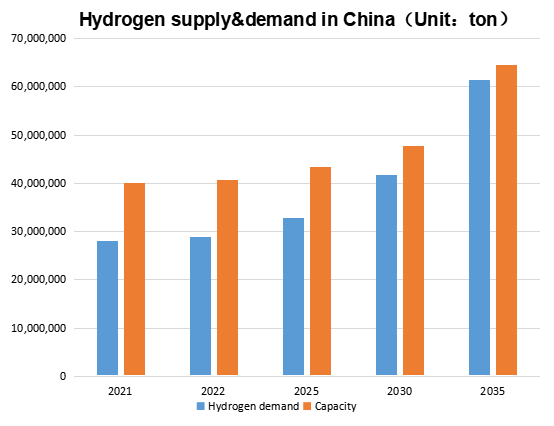
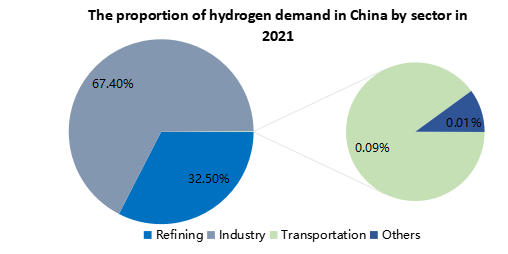
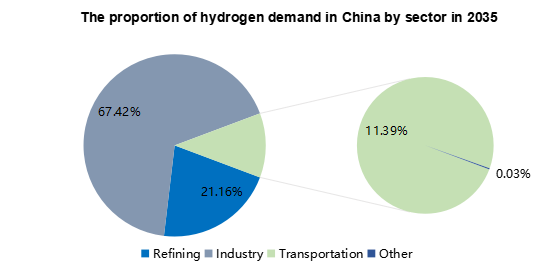
In China, with the promotion of carbon neutrality policy, China's hydrogen energy industry develop rapidly in recent years. According to TD, the demand for hydrogen is currently dominated by industry sector (as a raw material for ammonia & methanol production, etc.), following by refining. At present, due to the high cost and inadequate infrastructure, the proportion of transportation in hydrogen demand is relatively low. However, with the rapid development in fuel cell commercial vehicles, TD considers that hydrogen demand in transportation would grow fast, and the proportion would increase as well.